之前的文章中讨论过了[[CountDownLatch详解| CountDownLatch]]的使用方法和原理。今天再来讨论一下CyclicBarrier,CyclicBarrier的使用场景其实和CountDownLatch非常相似,用法也非常像,唯一地区别就是,不像CountDownLatch那样用一次就没了,CyclicBarrier可以重复使用。就像它名字的含义:“可以重复使用的栅栏”。
1. CyclicBarrier的使用 首先看看JavaDoc中给出的例子:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 class Solver { final int N; final float [][] data; final CyclicBarrier barrier; class Worker implements Runnable { int myRow; Worker(int row) { myRow = row; } public void run () { while (!done()) { processRow(myRow); try { barrier.await(); } catch (InterruptedException ex) { return ; } catch (BrokenBarrierException ex) { return ; } } } } public Solver (float [][] matrix) { data = matrix; N = matrix.length; Runnable barrierAction = new Runnable () { public void run () { mergeRows(...); }}; barrier = new CyclicBarrier (N, barrierAction); List<Thread> threads = new ArrayList <Thread>(N); for (int i = 0 ; i < N; i++) { Thread thread = new Thread (new Worker (i)); threads.add(thread); thread.start(); } for (Thread thread : threads) thread.join(); } } }
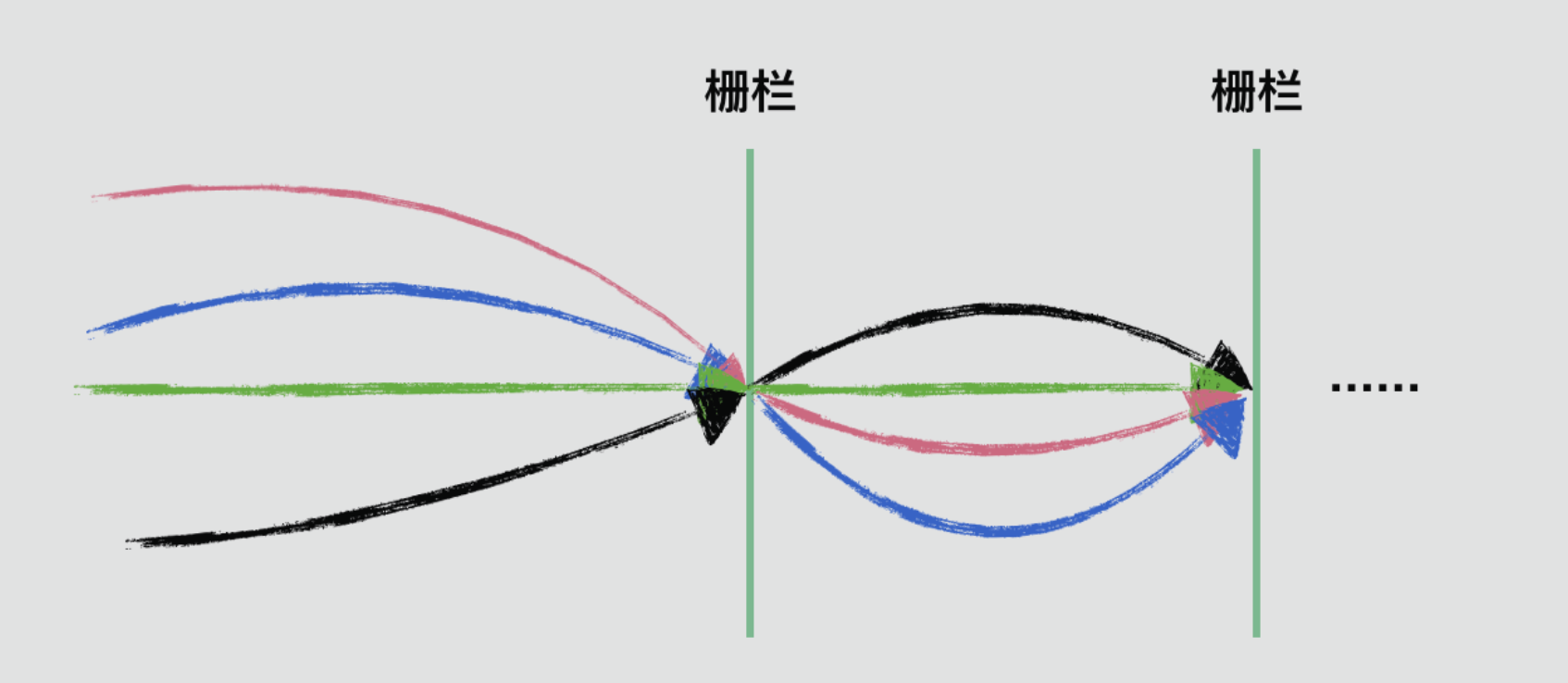
以上代码的目的是并行处理二维数组,使用CyclicBarrier进行同步,当所有行处理完,再进行合并操作。从以上示例代码可以看出CyclicBarrier的用法为使用await()。当await()的线程数量满足条件后,则会放行所有await()的线程。在放行之后又await()的将继续阻塞等待下一轮满足条件再放行。如下图:
2. 源码分析 2.1 首先看其成员变量和构造方法 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 public class CyclicBarrier { private static class Generation { boolean broken = false ; } private final ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock (); private final Condition trip = lock.newCondition(); private final int parties; private final Runnable barrierCommand; private Generation generation = new Generation (); private int count; public CyclicBarrier (int parties, Runnable barrierAction) { if (parties <= 0 ) throw new IllegalArgumentException (); this .parties = parties; this .count = parties; this .barrierCommand = barrierAction; } public CyclicBarrier (int parties) { this (parties, null ); } }
通过对其成员变量的认识,不难看出CyclicBarrier是基于ReentrantLock和Condition来实现的阻塞和释放,使用parties和count来记录参与的线程数和完成的线程数。引入了“代”的概念来实现栅栏的循环利用。
2.1 await() 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 public int await () throws InterruptedException, BrokenBarrierException { try { return dowait(false , 0L ); } catch (TimeoutException toe) { throw new Error (toe); } } public int await (long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException, BrokenBarrierException, TimeoutException { return dowait(true , unit.toNanos(timeout)); } private int dowait (boolean timed, long nanos) throws InterruptedException, BrokenBarrierException,TimeoutException { final ReentrantLock lock = this .lock; lock.lock(); try { final Generation g = generation; if (g.broken) throw new BrokenBarrierException (); if (Thread.interrupted()) { breakBarrier(); throw new InterruptedException (); } int index = --count; if (index == 0 ) { boolean ranAction = false ; try { final Runnable command = barrierCommand; if (command != null ) command.run(); ranAction = true ; nextGeneration(); return 0 ; } finally { if (!ranAction) breakBarrier(); } } for (;;) { try { if (!timed) trip.await(); else if (nanos > 0L ) nanos = trip.awaitNanos(nanos); } catch (InterruptedException ie) { if (g == generation && ! g.broken) { breakBarrier(); throw ie; } else { Thread.currentThread().interrupt(); } } if (g.broken) throw new BrokenBarrierException (); if (g != generation) return index; if (timed && nanos <= 0L ) { breakBarrier(); throw new TimeoutException (); } } } finally { lock.unlock(); } }
以上是await()的整体流程,接下来看其中的一些操作的细节:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 private void nextGeneration () { trip.signalAll(); count = parties; generation = new Generation (); } private void breakBarrier () { generation.broken = true ; count = parties; trip.signalAll(); } public void reset () { final ReentrantLock lock = this .lock; lock.lock(); try { breakBarrier(); nextGeneration(); } finally { lock.unlock(); } } public int getNumberWaiting () { final ReentrantLock lock = this .lock; lock.lock(); try { return parties - count; } finally { lock.unlock(); } } public int getParties () { return parties; } public boolean isBroken () { final ReentrantLock lock = this .lock; lock.lock(); try { return generation.broken; } finally { lock.unlock(); } }
思考:CyclicBarrier中,那些情况下会打破栅栏?
对于这个问题,直接查看那些地方调用了breakBarrier()方法即可。根据源码可知,打破栅栏的情况有以下几种:
线程被中断;
超时;
调用reset()方法。